Integrate with Keras¶
Keras is an API designed for human beings, not machines. Keras follows best practices for reducing cognitive load: it offers consistent & simple APIs, it minimizes the number of user actions required for common use cases, and it provides clear & actionable error messages. It also has extensive documentation and developer guides.
Comet automatically logs metrics, parameters, and histograms, and more from your Keras code.
Start logging¶
Log automatically¶
By integrating with Keras, Comet automatically logs the following items:
- Model and graph description
- Steps and epochs
- Metrics (such as loss and accuracy)
- Hyperparameters
- Optimizer Parameters (such as the learning rate, beta decay rate, and more)
- Number of trainable parameters
- Histograms for weights and biases
- Histograms for activations
- Histograms for gradients
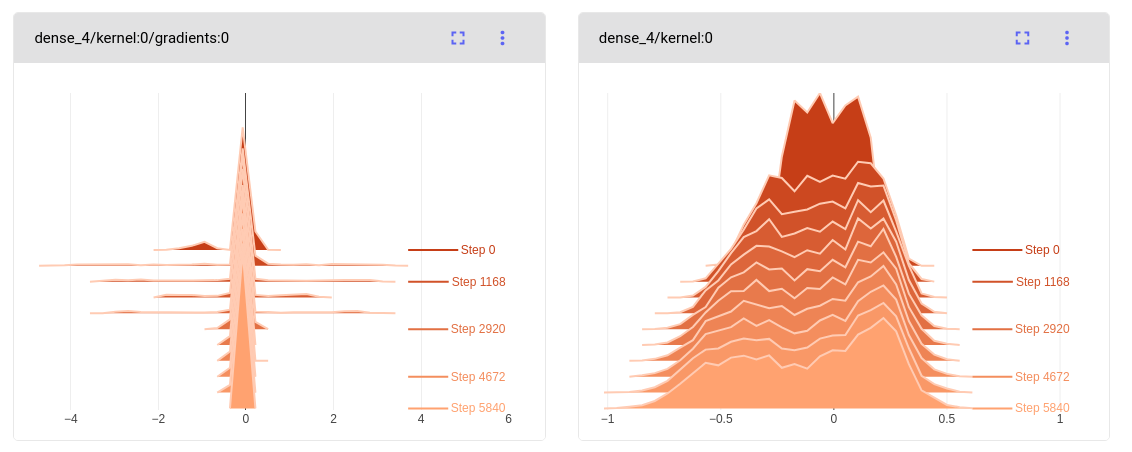
Log histograms automatically¶
By integrating with Keras, Comet automatically logs histograms for:
- Weights and biases
- Gradients
- Activations
These histograms appear on the Histogram tab in the single experiment pages:
The histograms for weights and biases are logged for all layers before training, and for every auto_histogram_epoch_rate epochs (default 1).
The histogram activations are logged for the selected input data or targets (comet.keras.histogram_activation_index_list with a default of the first pattern), at the selected layers (comet.keras.histogram_activation_layer_list with a default of the last layer).
For activation histograms:
| Item | Configuration Setting |
|---|---|
| which inputs | comet.keras.histogram_activation_index_list |
| which layers | comet.keras.histogram_activation_layer_list |
Info
To automatically log activations, you must be using TensorFlow, version 1.13 or higher. Inputs must be in a tensor or numpy format (for example, DataSets are not yet supported). Note that logging activations from an input layer do not work with TensorFlow version 1.
The histogram gradients of the weights and biases with respect to the loss are logged for the selected inputs or targets (comet.keras.histogram_gradient_index_list with a default of the first pattern), at the selected layers (comet.keras.histogram_gradient_layer_list with a default of the last layer).
For gradient histograms:
| Item | Configuration Setting |
|---|---|
| which inputs | comet.keras.histogram_gradient_index_list |
| which layers | comet.keras.histogram_gradient_layer_list |
Info
To automatically log gradients, you must be using TensorFlow, version 2.2.1 or higher, or Keras 2.4.3 and higher. Inputs and targets must be in a tensor or numpy format (e.g., DataSets are not yet supported).
Each input of the index lists is composed of an empty string or a list of index positions. If more than one index is given, separate the values with a comma.
For example, to indicate that you would like to log the activations for the first three input data examples, use:
export COMET_KERAS_HISTOGRAM_ACTIVATION_INDEX_LIST="0,1,2"
Each item in the layer list is composed of a list of index positions, negative index positions, or layer names. If more than one value is given, separate them with a comma.
For example, to indicate that you would like to log the gradients at the first layer, last layer, and a layer named "hidden", use:
export COMET_KERAS_HISTOGRAM_GRADIENT_LAYER_LIST="0,-1,hidden"
Similarly, if you would like to log the activations from these layers use:
export COMET_KERAS_HISTOGRAM_ACTIVATION_LAYER_LIST="0,-1,hidden"
Each of the histograms logged can have a "prefix" attached to the histogram name in the UI. The prefix is set through the configuration setting comet.keras.histogram_name_prefix and can be composed of any of the following components:
| Histogram name prefix component | Meaning |
|---|---|
{model_name} | Name of the Keras model |
{layer_name} | Name of the Keras layer |
{layer_num} | Number of the Keras layer |
{max_digits} | Number of digits in last Keras layer |
By default, the prefix is {layer_num:0{max_digits}d} (using Python's formatting syntax) which would give prefixes like:
01/input/kernel:0
05/hidden/bias:0
10/output/activation:all
Finally, you can control the following items as well:
| Item | Meaning | Default value |
|---|---|---|
| comet.keras.histogram_batch_size | number of patterns to process at once when logging all | 1000 |
| comet.logging.metrics_ignore | names of metrics to ignore | keras:batch_size, keras:batch_batch |
| comet.logging.parameters_ignore | names of parameters to ignore | keras:verbose, keras:do_validation, keras:validation_steps |
For more details on passing in parameters to the experiment, please see Experiment(). For more details on setting up configuration variables, see Python Configuration.
Validation metrics¶
If you provide validation_data to the Keras fit function, metrics will be logged for each validation batch with the validate prefix. For example, the following batch metrics will be logged:
lossfor every epochbatch_lossfor every training batch (depending on the value ofauto_metric_step_rate)validate_batch_lossfor every validation batch (depending on the value ofauto_metric_step_rate)
The validation metrics are logged with their own step to avoid interfering with the training metrics.
Warning
Note that this behavior was changed in the Comet Python SDK 3.33.6. Previously, the validation metrics were logged with the same steps as the training metrics, and the step was increased for every training or validation batch.
If you are resuming the training, you will need to manually set the validation step in the Keras callback. Here is an example of how to properly set everything up:
experiment = ExistingExperiment(experiment_key=COMET_EXPERIMENT_KEY)
experiment.set_step(LAST_TRAINING_STEP)
experiment.set_epoch(LAST_EPOCH)
keras_callback = experiment.get_callback(
"keras", initial_validation_step=LAST_VALIDATION_STEP
)
# Resume training
model.fit(
x_train,
y_train,
epochs=TOTAL_EPOCHS,
initial_epoch=LAST_EPOCH,
validation_data=(x_test, y_test),
callbacks=[keras_callback],
)
End-to-end example¶
Here is a simple end-to-end Keras example that uses a Dense neural network on the MNIST dataset.
For more examples using Keras, see our examples GitHub repository.
Install dependencies¶
pip install comet_ml tensorflow numpy
Run the example¶
from comet_ml import Experiment
#create an experiment with your api key
experiment = Experiment(
project_name='mnist',
auto_histogram_weight_logging=True,
auto_histogram_gradient_logging=True,
auto_histogram_activation_logging=True,
)
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Dropout
from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping
batch_size = 128
num_classes = 10
epochs = 20
num_nodes = 64
optimizer = 'adam'
activation = 'relu'
# the data, shuffled and split between train and test sets
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
x_train = x_train.reshape(60000, 784)
x_test = x_test.reshape(10000, 784)
x_train = x_train.astype('float32')
x_test = x_test.astype('float32')
x_train /= 255
x_test /= 255
print(x_train.shape[0], 'train samples')
print(x_test.shape[0], 'test samples')
# convert class vectors to binary class matrices
y_train = keras.utils.to_categorical(y_train, num_classes)
y_test = keras.utils.to_categorical(y_test, num_classes)
#these will all get logged
params={'batch_size':batch_size,
'epochs':epochs,
'layer1_type':'Dense',
'layer1_num_nodes':num_nodes,
'layer1_activation':activation,
'optimizer':optimizer
}
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(num_nodes, activation='relu', input_shape=(784,)))
#model.add(Dense(256, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(num_classes, activation='softmax'))
#print model.summary() to preserve automatically in `Output` tab
print(model.summary())
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy',
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
#will log metrics with the prefix 'train_'
with experiment.train():
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train,
batch_size=batch_size,
epochs=epochs,
verbose=1,
validation_data=(x_test, y_test),
callbacks=[EarlyStopping(monitor='val_loss', min_delta=1e-4,patience=3, verbose=1, mode='auto')])
#will log metrics with the prefix 'test_'
with experiment.test():
loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test)
metrics = {
'loss':loss,
'accuracy':accuracy
}
experiment.log_metrics(metrics)
experiment.log_parameters(params)
experiment.log_dataset_hash(x_train) #creates and logs a hash of your data
Try it out!¶
Don't just take our word for it, try it out for yourself.
- For more examples using Keras, see our examples GitHub repository.
- Run the end-to-end example above in Colab:
Use the Comet Keras callback¶
Comet logs your experiment through a callback executed when you run model.fit() in Keras. You do not need to add this callback yourself, we do it for you automatically. However, if you ever need to access the callback manually, simply call experiment.get_keras_callback().
You can use this callback to log additional data to Comet such as model checkpoints, images, audio, and more, as Experiment Assets, Models or Artifacts.
Report manually¶
If you want to log data that isn't already automatically logged or handled by the Keras callback, check out the logging methods available in Comet's Experiment object.
Configure Comet for Keras¶
You can control what is automatically logged by Comet through an experiment parameter, environment variable, or configuration setting:
| Item | Experiment Parameter | Environment Setting | Configuration Setting |
|---|---|---|---|
| model/graph description | log_graph | COMET_AUTO_LOG_GRAPH | comet.auto_log.graph |
| metrics | auto_metric_logging | COMET_AUTO_LOG_METRICS | comet.auto_log.metrics |
| metric logging rate | auto_metric_step_rate | COMET_AUTO_LOG_METRIC_STEP_RATE | comet.auto_log.metric_step_rate |
| hyperparameters | auto_param_logging | COMET_AUTO_LOG_PARAMETERS | comet.auto_log.parameters |
| command-line arguments | parse_args | COMET_AUTO_LOG_CLI_ARGUMENTS | comet.auto_log.cli_arguments |
| weights/biases | auto_histogram_weight_logging | COMET_AUTO_LOG_HISTOGRAM_WEIGHTS | comet.auto_log.histogram_weights |
| gradients | auto_histogram_gradient_logging | COMET_AUTO_LOG_HISTOGRAM_GRADIENTS | comet.auto_log.histogram_gradients |
| activations | auto_histogram_activation_logging | COMET_AUTO_LOG_HISTOGRAM_ACTIVATIONS | comet.auto_log.histogram_activations |
| histogram logging rate | auto_histogram_epoch_rate | COMET_AUTO_LOG_HISTOGRAM_EPOCH_RATE | comet.auto_log.histogram_epoch_rate |
For more information about using environment parameters in Comet, see Configure Comet.
In addition, you can control exactly which inputs at which layers are logged for activations and gradient histogram logging.